Other Options
| Order Qty |
Price | Qty for Discount |
Discount Price |
Total Savings |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
NewPath Learning Properties & States of Matter Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-01 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Atoms & Chemical Bonding Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-08 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||
|
NewPath Learning Elements & the Periodic Table Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-06 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Chemical Reactions Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-07 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Forces & Motion Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-03 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Work, Power & Simple Machines Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-05 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Sound Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-04 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Light & Optics Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-09 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Electricity & Magnetism Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-10 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||
Additional Details
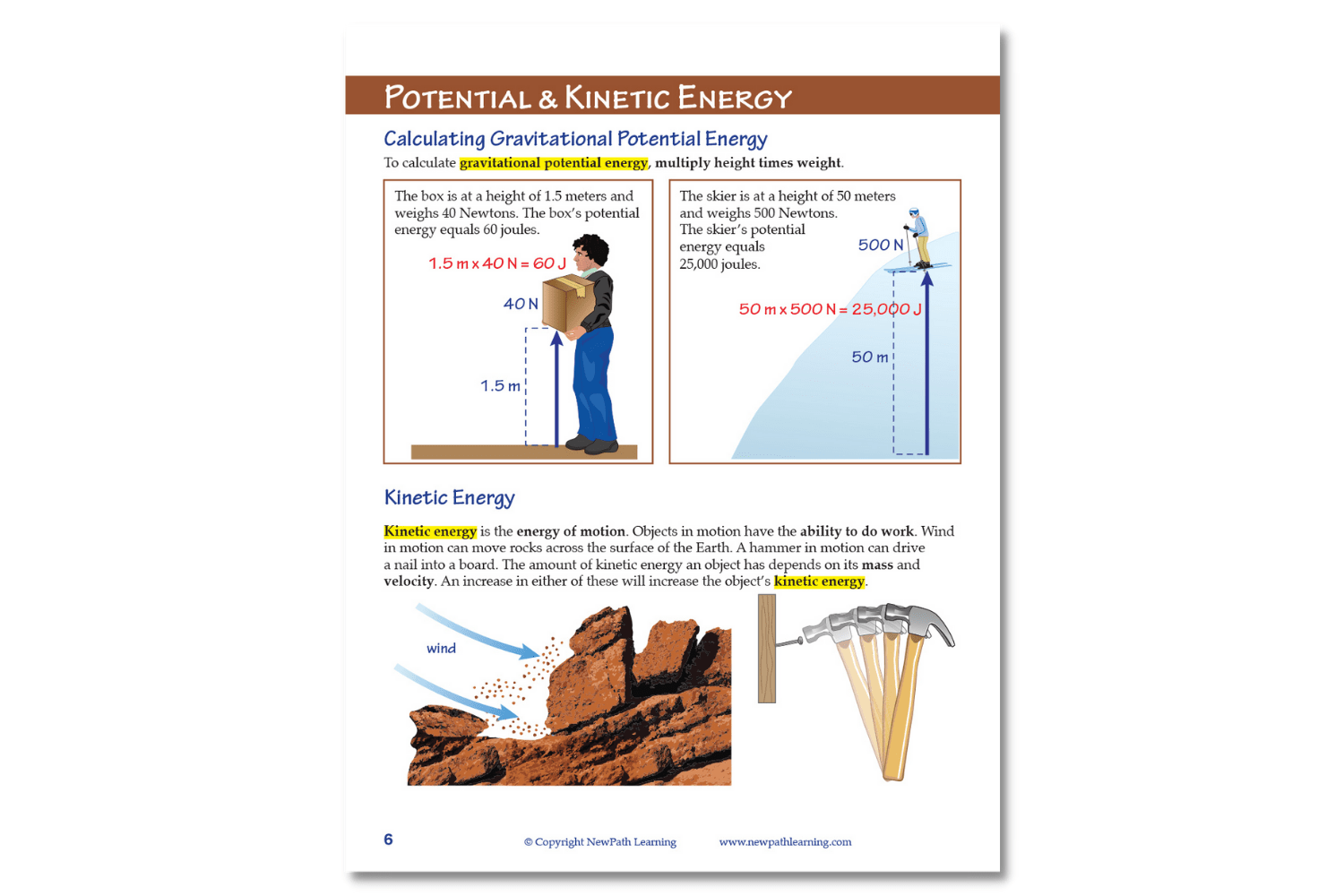
The NewPath Learning Energy: Forms & Changes Learning Guide turns the complex topic into an easy-to-learn, visually captivating, and engaging guide page by page! In the NewPath Learning Guide, you'll find self-directed readings, easy-to-follow illustrated explanations, guiding questions, inquiry-based activities, a lab investigation, key vocabulary review, and assessment review questions along with a post-test. The NewPath Learning Guide allows students to write directly in them and is designed for Grades 6-10.
This 44 page NewPath Learning Energy: Forms & Changes Learning Guide covers the following topics:
- Introduction to Energy
- Potential Energy
- Kinetic Energy
- Forms of Energy
- Energy Transformation
- Conservation of Energy
- Heat & Heat Technology
- Sources of Energy – Nonrenewable
- Sources of Energy - Renewable
- Vocabulary Review
Be confident knowing the NewPath Learning Guide covers Middle School Next Generation Science Standards.
Standards
Middle School (Grades 6, 7, 8) NGSS Correlations
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-PS1. | Matter and Its Interactions - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS1.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS3.A: | Definitions of Energy |
| INDICATOR | PS3.A:1. | The term “heat” as used in everyday language refers both to thermal motion (the motion of atoms or molecules within a substance) and radiation (particularly infrared and light). In science, heat is used only for this second meaning; it refers to energy transferred when two objects or systems are at different temperatures. (secondary to MS-PS1-4) |
| INDICATOR | PS3.A:2. | Temperature is not a measure of energy; the relationship between the temperature and the total energy of a system depends on the types, states, and amounts of matter present. (secondary to MS-PS1-4) |
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-PS3. | Energy - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS3-5. | Construct, use, and present arguments to support the claim that when the motion energy of an object changes, energy is transferred to or from the object. |
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-PS3. | Energy - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS3.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS3.A: | Definitions of Energy |
| INDICATOR | PS3.A:1. | Motion energy is properly called kinetic energy; it is proportional to the mass of the moving object and grows with the square of its speed. (MS- PS3-1) |
| INDICATOR | PS3.A:3. | Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles of matter. The relationship between the temperature and the total energy of a system depends on the types, states, and amounts of matter present. (MS-PS3-3), (MS-PS3-4) |
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-PS3. | Energy - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS3.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS3.B: | Conservation of Energy and Energy Transfer |
| INDICATOR | PS3.B:1. | When the motion energy of an object changes, there is inevitably some other change in energy at the same time. (MS-PS3-5) |
| INDICATOR | PS3.B:3. | Energy is spontaneously transferred out of hotter regions or objects and into colder ones. (MS-PS3-3) |
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-PS3. | Energy - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS3.CC. | Crosscutting Concepts |
| ELEMENT | MS-PS3.CC.3. | Energy and Matter |
| INDICATOR | MS-PS3.CC.3.1. | Energy may take different forms (e.g. energy in fields, thermal energy, energy of motion). (MS-PS3-5) |
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-ESS. | EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-ESS3. | Earth and Human Activity - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-ESS3.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | ESS3.A: | Natural Resources |
| INDICATOR | ESS3.A:1. | Humans depend on Earth’s land, ocean, atmosphere, and biosphere for many different resources. Minerals, fresh water, and biosphere resources are limited, and many are not renewable or replaceable over human lifetimes. These resources are distributed unevenly around the planet as a result of past geologic processes. (MS-ESS3-1) |
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-ESS. | EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-ESS3. | Earth and Human Activity - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-ESS3.CETS. | Connections to Engineering, Technology, and Applications of Science |
| ELEMENT | MS-ESS3.CETS.1. | Influence of Science, Engineering, and Technology on Society and the Natural World |
| INDICATOR | MS-ESS3.CETS.1.1. | All human activity draws on natural resources and has both short and long-term consequences, positive as well as negative, for the health of people and the natural environment. (MS-ESS3-1), (MS-ESS3-4) |
High School (Grades 9) NGSS Correlations
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS1. | Matter and Its Interactions - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS1.CC. | Crosscutting Concepts |
| ELEMENT | HS-PS1.CC.2. | Energy and Matter |
| INDICATOR | HS-PS1.CC.2.3. | Changes of energy and matter in a system can be described in terms of energy and matter flows into, out of, and within that system. (HS-PS1-4) |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS3. | Energy - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS3-1. | Create a computational model to calculate the change in the energy of one component in a system when the change in energy of the other component(s) and energy flows in and out of the system are known. |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS3-3. | Design, build, and refine a device that works within given constraints to convert one form of energy into another form of energy.* |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS3. | Energy - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS3.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS3.A: | Definitions of Energy |
| INDICATOR | PS3.A:1. | Energy is a quantitative property of a system that depends on the motion and interactions of matter and radiation within that system. That there is a single quantity called energy is due to the fact that a system’’s total energy is conserved, even as, within the system, energy is continually transferred from one object to another and between its various possible forms. (HS-PS3-1), (HS-PS3-2) |
| INDICATOR | PS3.A:2. | At the macroscopic scale, energy manifests itself in multiple ways, such as in motion, sound, light, and thermal energy. (HS-PS3-2) (HS-PS3-3) |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS3. | Energy - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS3.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS3.B: | Conservation of Energy and Energy Transfer |
| INDICATOR | PS3.B:1. | Conservation of energy means that the total change of energy in any system is always equal to the total energy transferred into or out of the system. (HS-PS3-1) |
| INDICATOR | PS3.B:2. | Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transported from one place to another and transferred between systems. (HS-PS3-1), (HS- PS3-4) |
| INDICATOR | PS3.B:3. | Mathematical expressions, which quantify how the stored energy in a system depends on its configuration (e.g. relative positions of charged particles, compression of a spring) and how kinetic energy depends on mass and speed, allow the concept of conservation of energy to be used to predict and describe system behavior. (HS-PS3-1) |
| INDICATOR | PS3.B:4. | The availability of energy limits what can occur in any system. (HS-PS3- 1) |
| INDICATOR | PS3.B:5. | Uncontrolled systems always evolve toward more stable states—that is, toward more uniform energy distribution (e.g., water flows downhill, objects hotter than their surrounding environment cool down). (HS-PS3-4) |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS3. | Energy - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS3.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS3.C: | Relationship Between Energy and Forces |
| INDICATOR | PS3.C:1. | When two objects interacting through a field change relative position, the energy stored in the field is changed. (HS-PS3-5) |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS3. | Energy - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS3.CC. | Crosscutting Concepts |
| ELEMENT | HS-PS3.CC.3. | Energy and Matter |
| INDICATOR | HS-PS3.CC.3.1. | Changes of energy and matter in a system can be described in terms of energy and matter flows into, out of, and within that system. (HS-PS3-3) |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-ESS. | EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-ESS1. | Earth’s Place in the Universe - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-ESS1.CC. | Crosscutting Concepts |
| ELEMENT | HS-ESS1.CC.3. | Energy and Matter |
| INDICATOR | HS-ESS1.CC.3.2. | In nuclear processes, atoms are not conserved, but the total number of protons plus neutrons is conserved. (HS-ESS1-3) |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-ESS. | EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-ESS3. | Earth and Human Activity - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-ESS3-2. | Evaluate competing design solutions for developing, managing, and utilizing energy and mineral resources based on cost-benefit ratios.* |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-ESS. | EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-ESS3. | Earth and Human Activity - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-ESS3.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | ESS3.C: | Human Impacts on Earth Systems |
| INDICATOR | ESS3.C:2. | Scientists and engineers can make major contributions by developing technologies that produce less pollution and waste and that preclude ecosystem degradation. (HS-ESS3-4) |