Other Options
| Order Qty |
Price | Qty for Discount |
Discount Price |
Total Savings |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
NewPath Learning Properties & States of Matter Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-01 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Atoms & Chemical Bonding Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-08 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||
|
NewPath Learning Elements & the Periodic Table Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-06 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Chemical Reactions Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-07 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Energy: Forms & Changes Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-02 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Forces & Motion Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-03 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Work, Power & Simple Machines Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-05 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Sound Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-04 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Electricity & Magnetism Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-10 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||
Additional Details
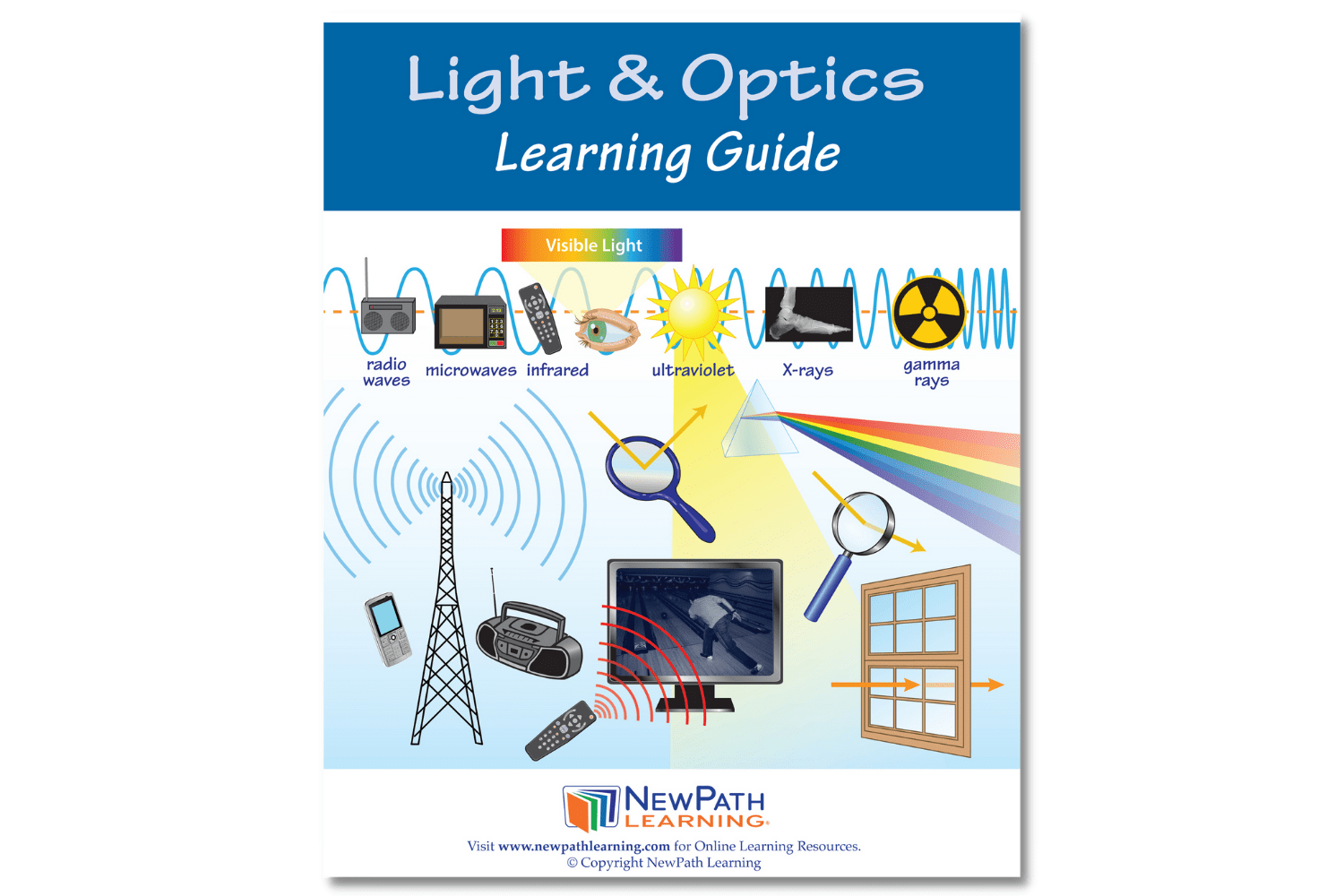
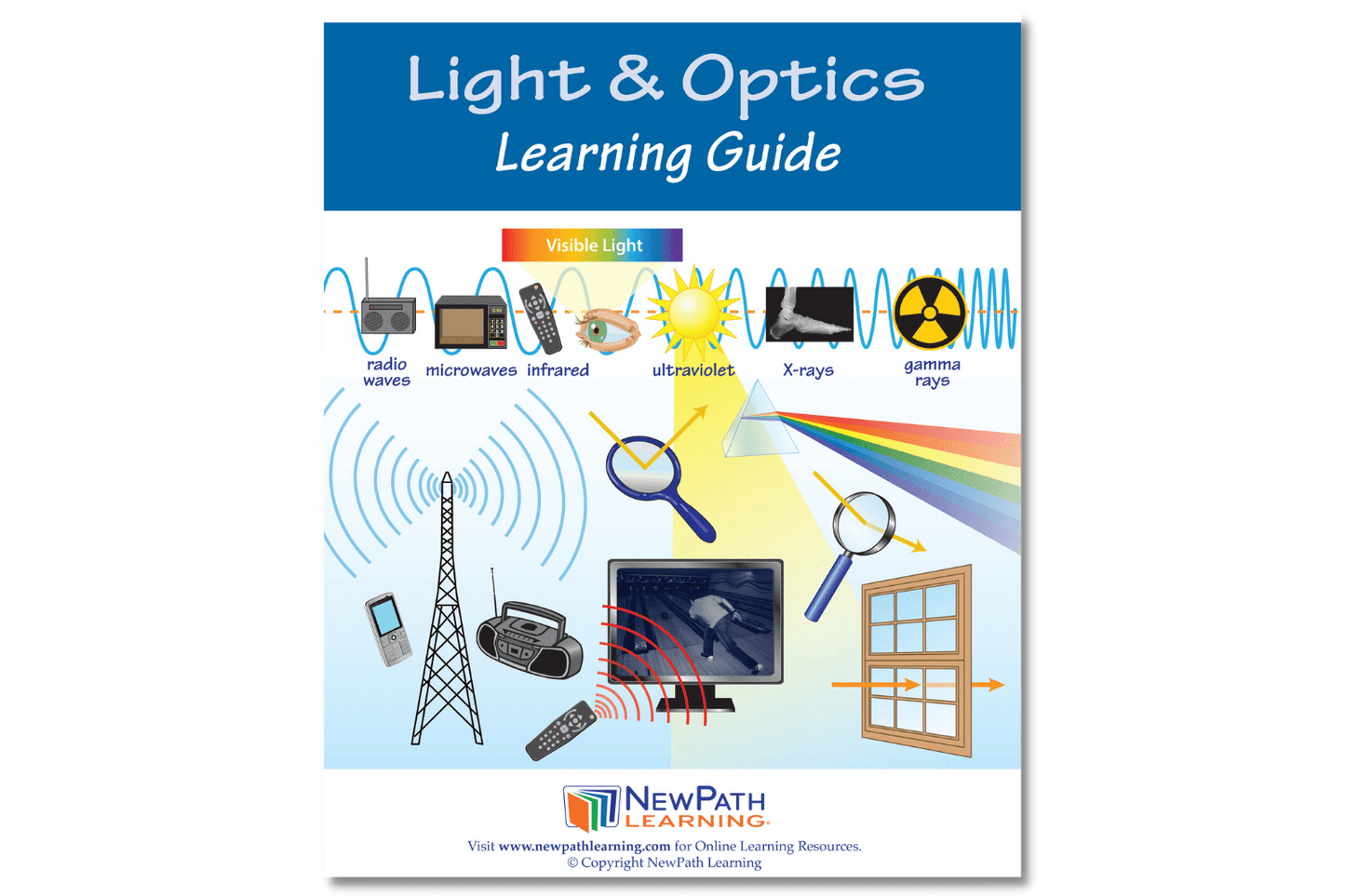
The NewPath Learning Light & Optics Learning Guide turns the complex topic into an easy-to-learn, visually captivating, and engaging guide page by page! In the NewPath Learning Guide, you'll find self-directed readings, easy-to-follow illustrated explanations, guiding questions, inquiry-based activities, a lab investigation, key vocabulary review, and assessment review questions along with a post-test. The NewPath Learning Guide allows students to write directly in them and is designed for Grades 6-10.
This 44 page NewPath Learning Light & Optics Learning Guide covers the following topics:
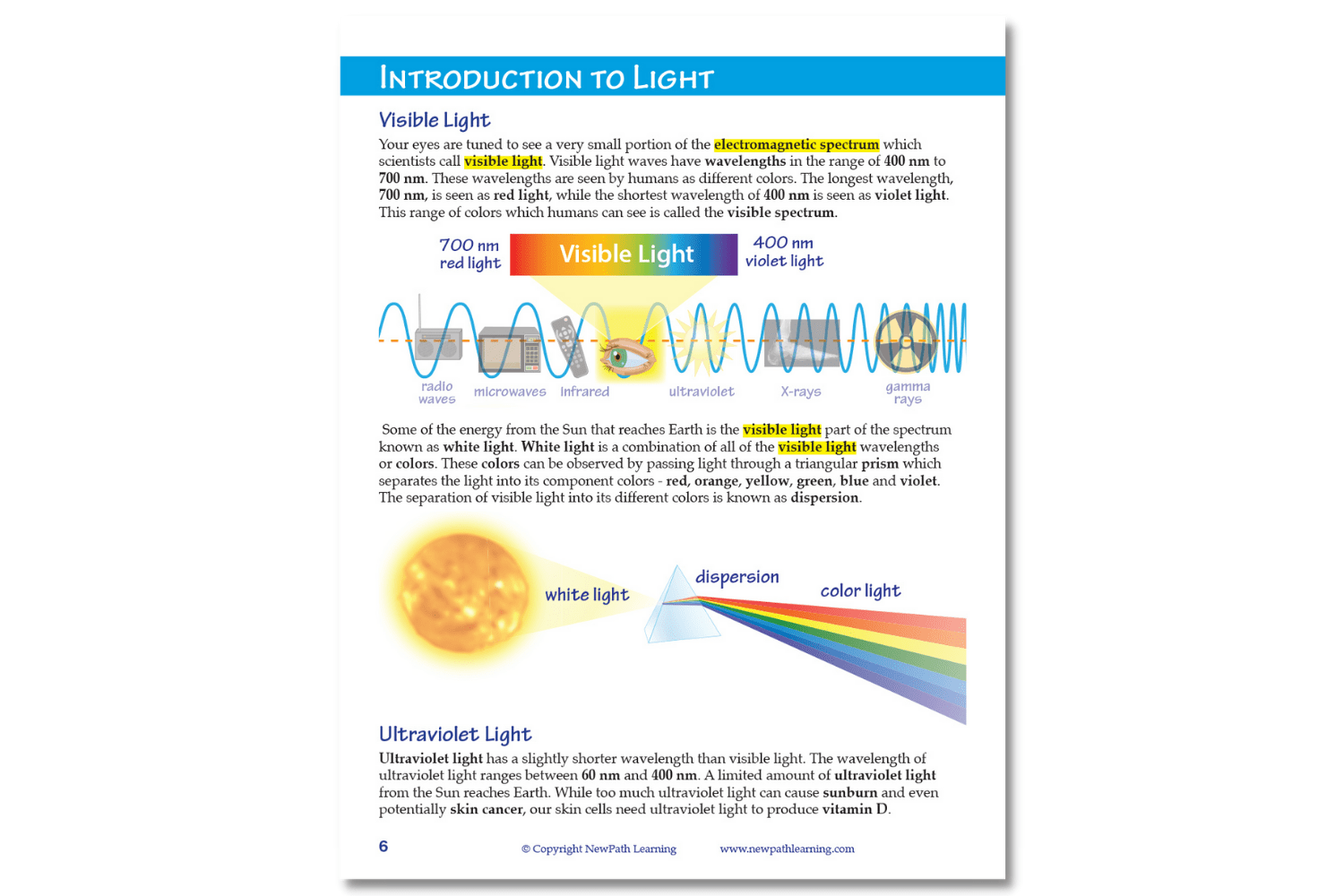
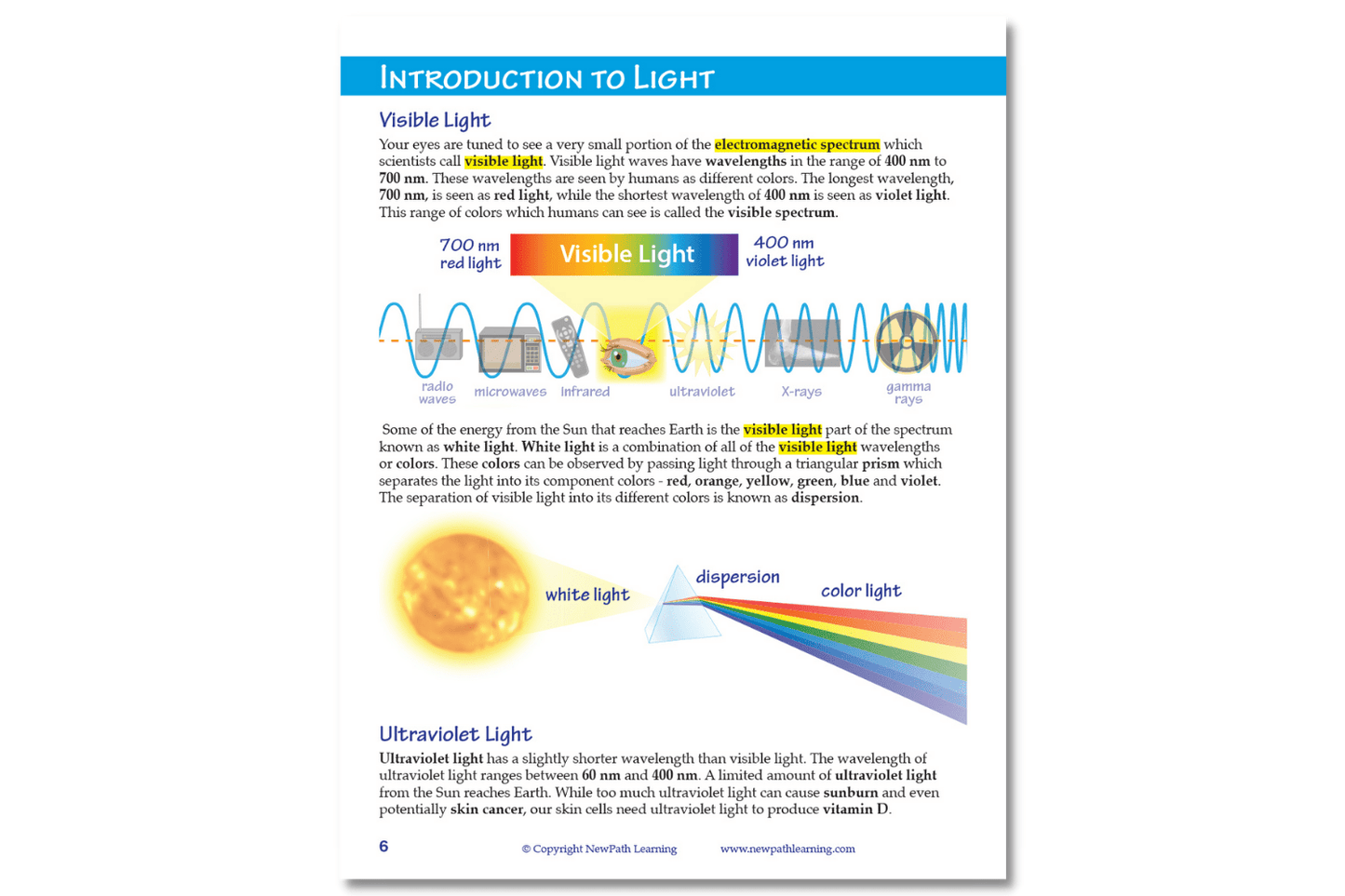
- Introduction to Light
- The EM Spectrum
- Transmission of Light
- Light & Color
- Interactions with Light
- Reflections & Mirrors
- Refraction & Lenses
- Light & the Human Eye (Vision)
- Light in Technology
- Vocabulary Review
Be confident knowing the NewPath Learning Guide covers Middle School Next Generation Science Standards.
Standards
Middle School (Grades 6, 7, 8) NGSS Correlations
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-PS3. | Energy - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS3.CC. | Crosscutting Concepts |
| ELEMENT | MS-PS3.CC.1. | Scale, Proportion, and Quantity |
| INDICATOR | MS-PS3.CC.1.1. | Proportional relationships (e.g. speed as the ratio of distance traveled to time taken) among different types of quantities provide information about the magnitude of properties and processes. (MS-PS3-1), (MS-PS3-4) |
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-PS4. | Waves and Their Applications in Technologies for Information Transfer - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS4-2. | Develop and use a model to describe that waves are reflected, absorbed, or transmitted through various materials. |
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-PS4. | Waves and Their Applications in Technologies for Information Transfer - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS4.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS4.A: | Wave Properties |
| INDICATOR | PS4.A:1. | A simple wave has a repeating pattern with a specific wavelength, frequency, and amplitude. (MS-PS4-1) |
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-PS4. | Waves and Their Applications in Technologies for Information Transfer - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS4.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS4.B: | Electromagnetic Radiation |
| INDICATOR | PS4.B:1. | When light shines on an object, it is reflected, absorbed, or transmitted through the object, depending on the object’s material and the frequency (color) of the light. (MS-PS4-2) |
| INDICATOR | PS4.B:2. | The path that light travels can be traced as straight lines, except at surfaces between different transparent materials (e.g., air and water, air and glass) where the light path bends. (MS-PS4-2) |
| INDICATOR | PS4.B:4. | However, because light can travel through space, it cannot be a matter wave, like sound or water waves. (MS-PS4-2) |
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-LS. | LIFE SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-LS1. | From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-LS1.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | LS1.D: | Information Processing |
| INDICATOR | LS1.D:1. | Each sense receptor responds to different inputs (electromagnetic, mechanical, chemical), transmitting them as signals that travel along nerve cells to the brain. The signals are then processed in the brain, resulting in immediate behaviors or memories. (MS-LS1-8) |
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-ESS. | EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-ESS1. | Earth’s Place in the Universe - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-ESS1.CETS. | Connections to Engineering, Technology, and Applications of Science |
| ELEMENT | MS-ESS1.CETS.1. | Interdependence of Science, Engineering, and Technology |
| INDICATOR | MS-ESS1.CETS.1.1. | Engineering advances have led to important discoveries in virtually every field of science and scientific discoveries have led to the development of entire industries and engineered systems. (MS-ESS1-3) |
High School (Grades 9) NGSS Correlations
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS2. | Motion and Stability: Forces and Interactions - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS2.SEP. | Science and Engineering Practices |
| ELEMENT | HS-PS2.SEP .1. | or test solutions to problems in 9–12 builds on K–8 experiences and progresses to include investigations that provide evidence for and test conceptual, mathematical, physical and empirical models. |
| INDICATOR | HS-PS2.SEP .1.1. | Plan and conduct an investigation individually and collaboratively to produce data to serve as the basis for evidence, and in the design: decide on types, how much, and accuracy of data needed to produce reliable measurements and consider limitations on the precision of the data (e.g., number of trials, cost, risk, time), and refine the design accordingly. (HS-PS2-5) |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS3. | Energy - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS3.SEP. | Science and Engineering Practices |
| ELEMENT | HS-PS3.SEP.2. | Planning and Carrying Out Investigations - Planning and carrying out investigations to answer questions or test solutions to problems in 9–12 builds on K–8 experiences and progresses to include investigations that provide evidence for and test conceptual, mathematical, physical, and empirical models. |
| INDICATOR | HS-PS3.SEP.2.1. | Plan and conduct an investigation individually and collaboratively to produce data to serve as the basis for evidence, and in the design: decide on types, how much, and accuracy of data needed to produce reliable measurements and consider limitations on the precision of the data (e.g., number of trials, cost, risk, time), and refine the design accordingly. (HS-PS3-4) |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS4. | Waves and Their Applications in Technologies for Information Transfer - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS4-1. | Use mathematical representations to support a claim regarding relationships among the frequency, wavelength, and speed of waves traveling in various media. |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS4-3. | Evaluate the claims, evidence, and reasoning behind the idea that electromagnetic radiation can be described either by a wave model or a particle model, and that for some situations one model is more useful than the other. |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS4-5. | Communicate technical information about how some technological devices use the principles of wave behavior and wave interactions with matter to transmit and capture information and energy. |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS4. | Waves and Their Applications in Technologies for Information Transfer - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS4.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS4.A: | Wave Properties |
| INDICATOR | PS4.A:1. | The wavelength and frequency of a wave are related to one another by the speed of travel of the wave, which depends on the type of wave and the medium through which it is passing. (HS-PS4-1) |
| INDICATOR | PS4.A:3. | [From the 3–5 grade band endpoints] Waves can add or cancel one another as they cross, depending on their relative phase (i.e., relative position of peaks and troughs of the waves), but they emerge unaffected by each other. (Boundary: The discussion at this grade level is qualitative only; it can be based on the fact that two different sounds can pass a location in different directions without getting mixed up.) (HS-PS4-3) |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS4. | Waves and Their Applications in Technologies for Information Transfer - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS4.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS4.B: | Electromagnetic Radiation |
| INDICATOR | PS4.B:1. | Electromagnetic radiation (e.g., radio, microwaves, light) can be modeled as a wave of changing electric and magnetic fields or as particles called photons. The wave model is useful for explaining many features of electromagnetic radiation, and the particle model explains other features. (HS-PS4-3) |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-LS. | LIFE SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-LS1. | From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-LS1.CC. | Crosscutting Concepts |
| ELEMENT | HS-LS1.CC.3. | Structure and Function |
| INDICATOR | HS-LS1.CC.3.1. | Investigating or designing new systems or structures requires a detailed examination of the properties of different materials, the structures of different components, and connections of components to reveal its function and/or solve a problem. (HS-LS1-1) |