Other Options
| Order Qty |
Price | Qty for Discount |
Discount Price |
Total Savings |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
NewPath Learning Atoms & Chemical Bonding Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-08 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||
|
NewPath Learning Elements & the Periodic Table Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-06 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Chemical Reactions Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-07 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Energy: Forms & Changes Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-02 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Forces & Motion Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-03 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Work, Power & Simple Machines Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-05 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Sound Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-04 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Light & Optics Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-09 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||

|
NewPath Learning Electricity & Magnetism Learning Guide Item # 21-2010-10 |
|
|
$9.95 | ||||
Additional Details
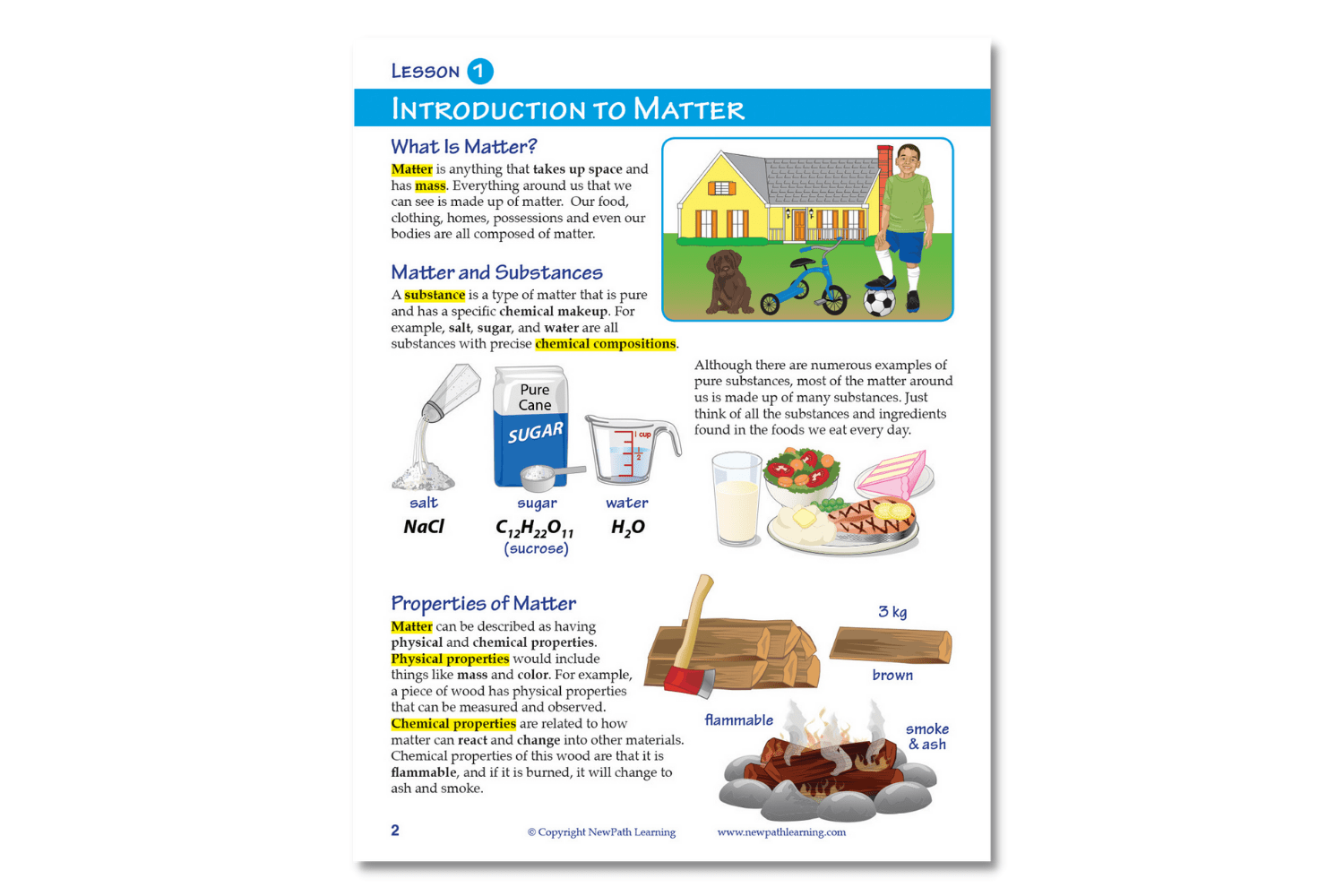
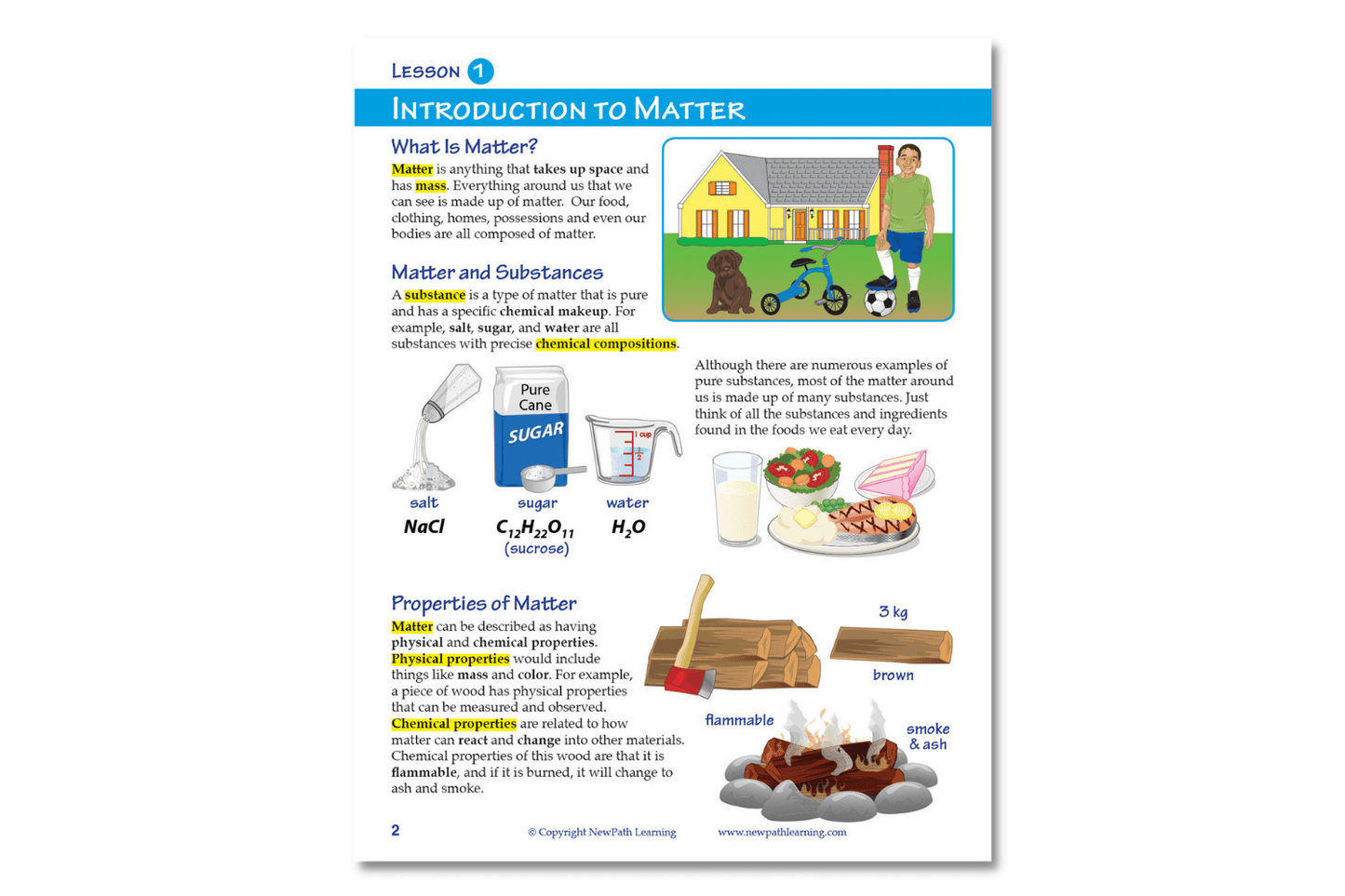
The NewPath Learning Properties & States of Matter Learning Guide turns the complex topic into an easy-to-learn, visually captivating, and engaging guide page by page! In the NewPath Learning Guide, you'll find self-directed readings, easy-to-follow illustrated explanations, guiding questions, inquiry-based activities, a lab investigation, key vocabulary review, and assessment review questions along with a post-test. The NewPath Learning Guide allows students to write directly in them and is designed for Grades 6-10.
This 44 page NewPath Learning Properties & States of Matter Learning Guide covers the following topics:
- What is Matter?
- Elements & Compounds
- Mixtures & Solutions
- States of Matter – Solids
- States of Matter – Liquids
- States of Matter – Gases
- Gas Laws
- Changes of State of Matter
- Measuring Matter
- Vocabulary Review
Be confident knowing the NewPath Learning Guide covers Middle School Next Generation Science Standards.
Standards
Middle School (Grades 6, 7, 8) NGSS Correlations
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-PS1. | Matter and Its Interactions - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS1-1. | Develop models to describe the atomic composition of simple molecules and extended structures. |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS1-4. | Develop a model that predicts and describes changes in particle motion, temperature, and state of a pure substance when thermal energy is added or removed. |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS1-6. | Undertake a design project to construct, test, and modify a device that either releases or absorbs thermal energy by chemical processes. |
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-PS1. | Matter and Its Interactions - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS1.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS1.A: | Structure and Properties of Matter |
| INDICATOR | PS1.A:1. | Substances are made from different types of atoms, which combine with one another in various ways. Atoms form molecules that range in size from two to thousands of atoms. (MS-PS1-1) |
| INDICATOR | PS1.A:2. | Each pure substance has characteristic physical and chemical properties (for any bulk quantity under given conditions) that can be used to identify it. (MS-PS1-2), (MS-PS1-3) |
| INDICATOR | PS1.A:3. | Gases and liquids are made of molecules or inert atoms that are moving about relative to each other. (MS-PS1-4) |
| INDICATOR | PS1.A:4. | In a liquid, the molecules are constantly in contact with others; in a gas, they are widely spaced except when they happen to collide. In a solid, atoms are closely spaced and may vibrate in position but do not change relative locations. (MS- PS1-4) |
| INDICATOR | PS1.A:5. | Solids may be formed from molecules, or they may be extended structures with repeating subunits (e.g., crystals). (MS-PS1-1) |
| INDICATOR | PS1.A:6. | The changes of state that occur with variations in temperature or pressure can be described and predicted using these models of matter. (MS-PS1-4) |
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-PS1. | Matter and Its Interactions - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS1.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS1.B: | Chemical Reactions |
| INDICATOR | PS1.B:3. | Some chemical reactions release energy, others store energy. (MS-PS1-6) |
| STRAND | NGSS.MS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | MS-PS3. | Energy - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | MS-PS3-4. | Plan an investigation to determine the relationships among the energy transferred, the type of matter, the mass, and the change in the average kinetic energy of the particles as measured by the temperature of the sample. |
High School (Grades 9) NGSS Correlations
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS1. | Matter and Its Interactions - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS1-4. | Develop a model to illustrate that the release or absorption of energy from a chemical reaction system depends upon the changes in total bond energy. |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS1. | Matter and Its Interactions - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS1.SEP . | Science and Engineering Practices |
| ELEMENT | HS-PS1.SEP .4. | Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions - Constructing explanations and designing solutions in 9–12 builds on K–8 experiences and progresses to explanations and designs that are supported by multiple and independent student- generated sources of evidence consistent with scientific ideas, principles, and theories. |
| INDICATOR | HS-PS1.SEP .4.2. | Construct and revise an explanation based on valid and reliable evidence obtained from a variety of sources (including students’ own investigations, models, theories, simulations, peer review) and the assumption that theories and laws that describe the natural world operate today as they did in the past and will continue to do so in the future. (HS-PS1-2) |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS1. | Matter and Its Interactions - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS1.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS1.A: | Structure and Properties of Matter |
| INDICATOR | PS1.A:1. | Each atom has a charged substructure consisting of a nucleus, which is made of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons. (HS-PS1-1) |
| INDICATOR | PS1.A:2. | The periodic table orders elements horizontally by the number of protons in the atom’s nucleus and places those with similar chemical properties in columns. The repeating patterns of this table reflect patterns of outer electron states. (HS- PS1-1), (HS-PS1-2) |
| INDICATOR | PS1.A:4. | Stable forms of matter are those in which the electric and magnetic field energy is minimized. A stable molecule has less energy than the same set of atoms separated; one must provide at least this energy in order to take the molecule apart. (HS-PS1-4) |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS1. | Matter and Its Interactions - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS1.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS1.B: | Chemical Reactions |
| INDICATOR | PS1.B:1. | Chemical processes, their rates, and whether or not energy is stored or released can be understood in terms of the collisions of molecules and the rearrangements of atoms into new molecules, with consequent changes in the sum of all bond energies in the set of molecules that are matched by changes in kinetic energy. (HS-PS1-4), (HS-PS1-5) |
| STRAND | NGSS.HS-PS. | PHYSICAL SCIENCE |
| TITLE | HS-PS3. | Energy - Students who demonstrate understanding can: |
| PERFORMANCE EXPECTATION / FOUNDATION | HS-PS3.DCI. | Disciplinary Core Ideas |
| ELEMENT | PS3.A: | Definitions of Energy |
| INDICATOR | PS3.A:3. | These relationships are better understood at the microscopic scale, at which all of the different manifestations of energy can be modeled as either motions of particles or energy stored in fields (which mediate interactions between particles). This last concept includes radiation, a phenomenon in which energy stored in fields moves across space. (HS-PS3-2) |